越来越多国家和地区的小麦主产区耕地被Cd污染。小麦极易吸收土壤中的Cd并积累在籽粒中,导致籽粒Cd含量超过中国标准(0.10 mg/kg)甚至国际标准(0.20 mg/kg)。作物营养元素管理是目前最快捷有效减少作物Cd积累的农艺措施之一。例如:合理施用锰(Mn)肥和铜(Cu)肥作为减少作物Cd吸收和积累的有效策略,但不同作物或品种间的作用和效应却不同。同时,Mn和Cu对小麦Cd吸收、转运和积累的影响及其机制仍未知。
我国新疆吐鲁番地区特有的矮秆波兰小麦(Triticum polonicum L., 2n=4x=28, AABB)含有矮秆、长粒和高千粒重等优异特性(Chai et al., 2021, 2022),是普通小麦(Triticum aestivum L., 2n=6x=42, AABBDD)遗传改良的优异种质资源。我们利用矮秆波兰小麦与主栽品种进行人工杂交,创制了系列株高适宜、长粒、高千粒重以及籽粒低Cd积累的优异育种新品系(图1),为普通小麦低Cd遗传改良拓宽了遗传基础和材料基础。为解析亲本矮秆波兰小麦Cd积累等属性,本研究在Cd处理条件下,对矮秆波兰小麦进行了缺失和添加Mn或Cu处理。

图1矮秆波兰小麦优异基因导入六倍体小麦后获得的部分育种材料
组织Cd浓度调查和植物非损伤检测系统(NMT)根系瞬时Cd吸收速率分析发现Mn缺失和Cu缺失促进了矮秆波兰小麦根部的Cd吸收(图2)。它们通过调节根系细胞细胞壁果胶和纤维素合成相关基因的表达增加细胞壁中的果胶和纤维素含量,进而提高根系细胞细胞壁对Cd的绑定;同时,上调Cd吸收相关基因的表达以及下调Cd转运相关基因的表达(图3),增强Cd的吸收以及可溶性组分和细胞器中的Cd积累。尽管Cu添加调节了根系细胞细胞壁纤维素合成相关基因的表达导致细胞壁绑定Cd的能力降低,但也上调了Cd吸收相关基因和下调了Cd外排相关基因来增加根系细胞细胞器和可溶性组分Cd含量(图3),最终不影响根部的Cd吸收和积累。Mn添加降低了根系Cd吸收;它主要通过降低液泡中Cd螯合相关基因的表达和增加Mn螯合相关基因的表达,竞争性地减少了根细胞器中的Cd积累。这些结果与之前课题组评价氮肥(Cheng et al., 2018, 2020, 2021)、铁肥(Yao et al., 2023)影响小麦Cd积累等结果综合,将更加丰富如何降低小麦籽粒Cd积累提供重要的理论依据。
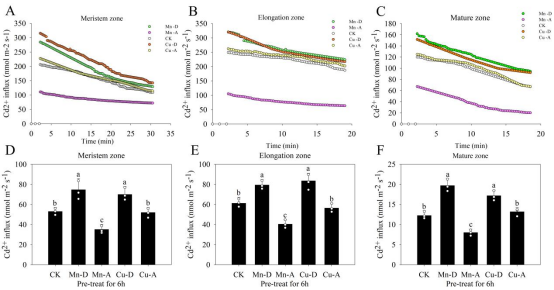
图2根部不同区域的Cd吸收瞬时速率
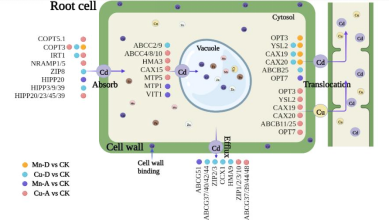
图3 Mn和Cu调节Cd吸收、转运和积累的相关基因
该研究结果以"Manganese and copper additions differently reduced cadmium uptake and accumulation in dwarf Polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.)"为题于2023年2月10日在国际著名期刊Journal of Hazardous Materials在线发表(中科院一区TOP)。四川农业大学小麦研究所作物遗传育种专业博士研究生陈兴为论文第一作者,王益教授和程怡然博士为论文通讯作者。该研究得到国家自然科学基金、中国博士后科学基金和四川省作物特色资源创造与利用重点实验室的资助。

相关文献
Chai S, Yao Q, Zhang X, Xiao X, Fan X, Zeng J, Sha L, Kang H, Zhang H, Li J, Zhou Y,Wang Y. 2021. The semi-dwarfing geneRht-dpfrom dwarf Polish wheat (Triticum polonicumL.) is the “green revolution” geneRht-B1b. BMC Genomics, 22: 63.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07367-x.
Chai S, Yao Q, Liu R, Xiang W, Xiao X, Fan X, Zeng J, Sha L, Kang H, Zhang H, Long D, Wu D, Zhou Y, Wang Y. 2022. Identification and validation of a major gene for kernel length at theP1 locus inTriticum polonicum. The Crop Journal, 10: 387-396.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.07.006.
Cheng Y, Wang C, Chai S, Shuai W, Sha L, Zhang H, Kang H, Fan X, Zeng J, Zhou Y, Wang Y. 2018. Ammonium N influences the uptakes, translocations, subcellular distributions and chemical forms of Cd and Zn to mediate the Cd/Zn interactions in dwarf polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.) seedlings. Chemosphere, 193: 1164-1171.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.058.
Cheng Y, Bao Y, Chen X, Yao Q, Wang C, Chai S, Zeng J, Fan X, Kang H, Sha L, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Wang Y. 2020. Different nitrogen forms differentially affect Cd uptake and accumulation in dwarf Polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.) seedlings. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400: 123209.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123209.
Cheng Y, Yang T, Xiang W, Li S, Fan X, Sha L, Kang H, Wu D, Zhang H, Zeng J, Zhou Y, Wang Y. 2021. Ammonium-nitrogen addition at the seedling stage does not reduce grain cadmium concentration in two common wheat (Triticum aestivumL.) cultivars. Environmental Pollution, 286: 117575.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117575.
Yao Q, Li W, Liu Y, Cheng Y, Xiao X, Long D, Zeng J, Wu D, Sha L, Fan X, Kang H, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Wang Y. 2023. FeCl3 and Fe2(SO4)3 differentially reduce Cd uptake and accumulation in Polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.) seedlings by exporting Cd from roots and limiting Cd binding in the root cell walls. Environmental Pollution, 317:120762.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120762.